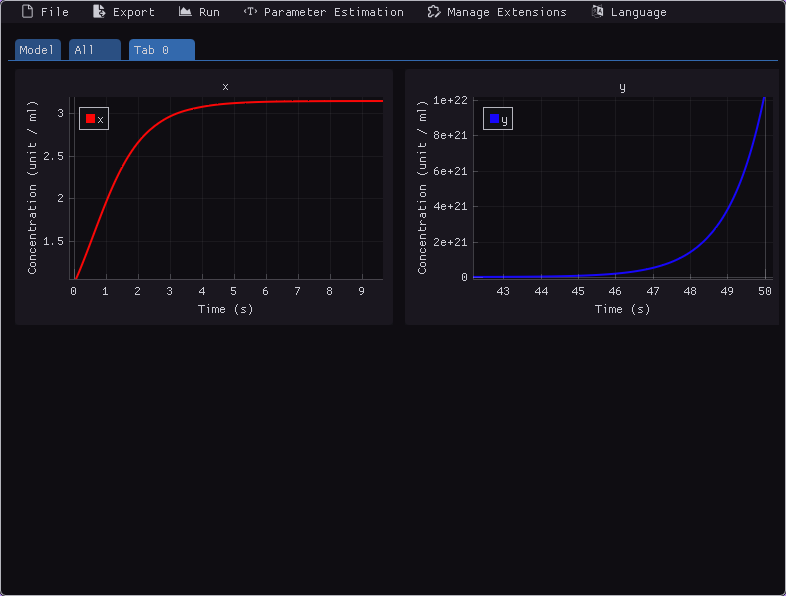
Functionalities
Node-based editor
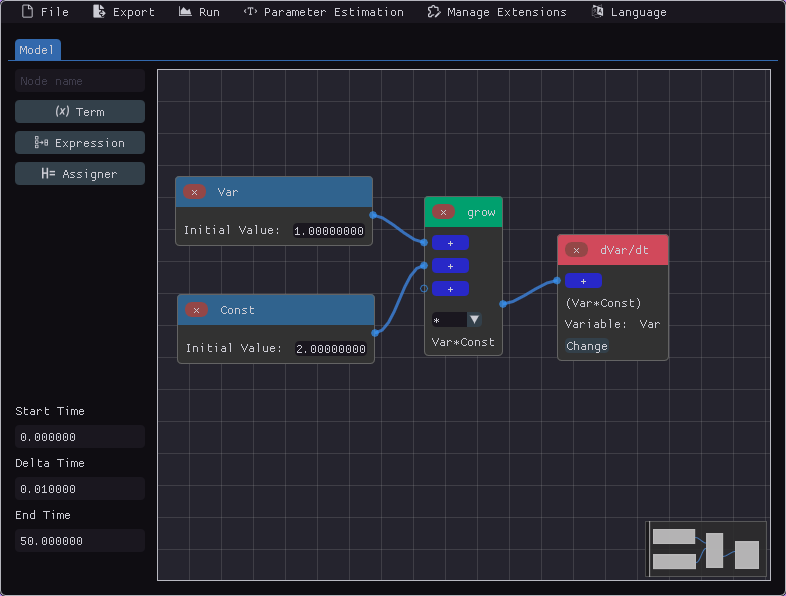
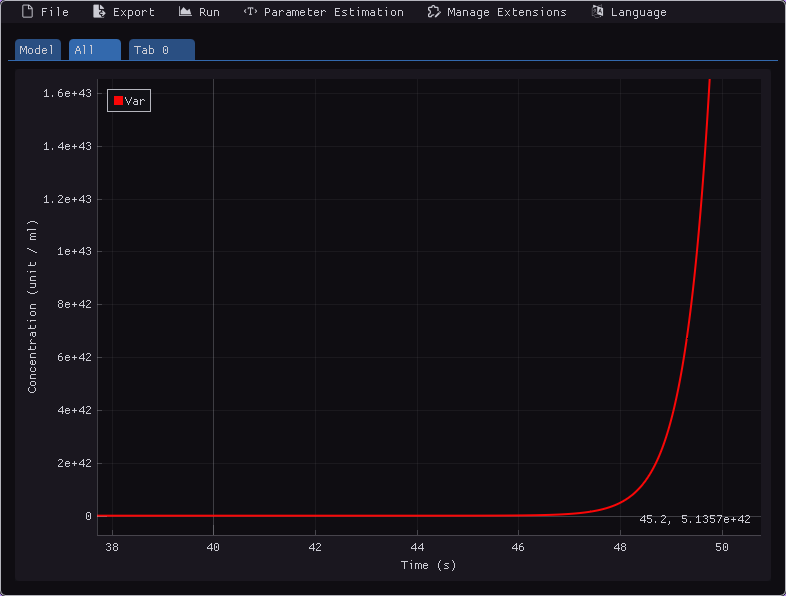
Plotting
Python code export and pdf export
# imports of scipy and numpy omitted
def initial_values() -> np.ndarray:
Var_0 = 1.0
return np.array((Var_0,))
def constants() -> list:
Const = 2.0
return [Const]
def variable_names() -> list[str]:
return ["Var"]
def system(t: np.float64, y: np.ndarray, *constants) -> np.ndarray:
Var, = y
Const, = constants
dVar_dt = Var*Const
return np.array([dVar_dt])
# Rest of the code used to simulate and plot to PDF omitted
Extensibility via Python code
Given the following Python code:
import math
@node
def sine(x):
return math.sin(x)
@node(format="$1 ^ $2")
def power(x, y):
return x ** y
By importing it in the Manage Extensions menu, you can use the defined nodes as if they were native, as in the image below.
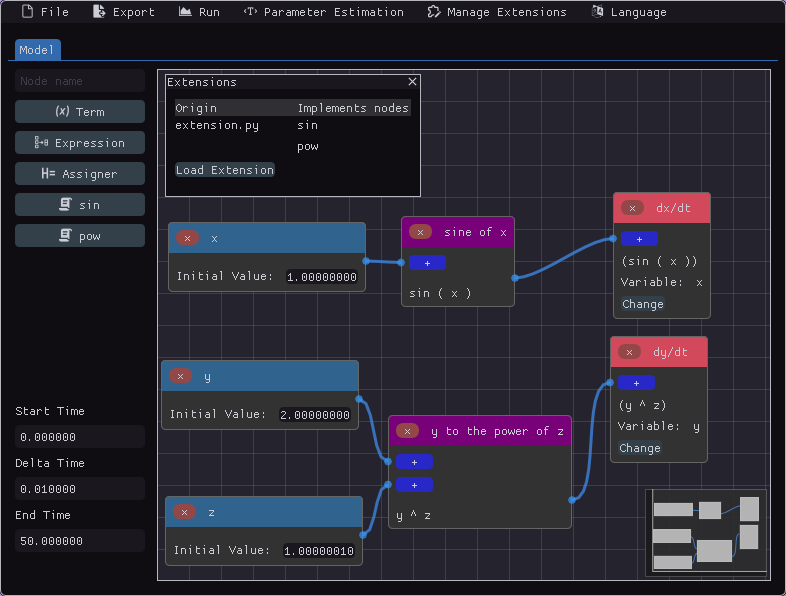
The code can be used to simulate just like native nodes.